Internet of Things (IoT): Bridging the Physical and Digital Worlds
What is the Internet of Things (IoT)?
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the network of interconnected devices that communicate and share data with each other via the internet. From smart thermostats to industrial sensors, IoT devices are facilitating seamless integration between the physical and digital worlds, creating opportunities for businesses to collect and analyze data to enhance efficiency and decision-making.
How IoT Works
IoT devices are equipped with sensors and software that enable them to gather and transmit data to centralized platforms or other devices. This data is processed and analyzed to generate actionable insights, allowing businesses to optimize processes, automate tasks, and improve decision-making. IoT’s reliance on cloud computing, edge computing, and machine learning ensures real-time data processing and efficient operations.
IoT in Business Operations
Businesses are leveraging IoT to streamline operations and reduce costs. In manufacturing, IoT sensors monitor equipment health, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing downtime. Similarly, in logistics, IoT trackers provide real-time updates on shipments, enhancing supply chain visibility and efficiency. By automating routine tasks, IoT allows businesses to focus on strategic initiatives.
Enhancing Customer Experiences
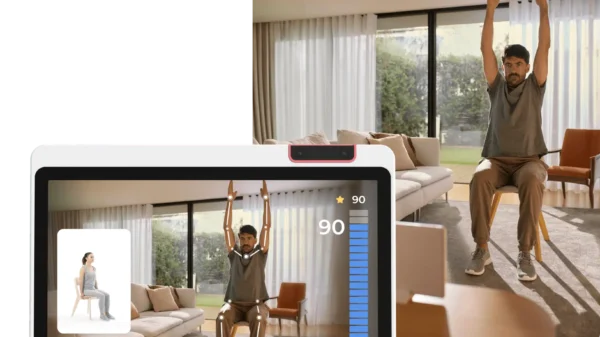
IoT plays a critical role in improving customer experiences by personalizing interactions and offering convenience. Smart devices, such as voice assistants and connected appliances, adapt to user preferences, creating tailored experiences. Retailers use IoT-enabled beacons to offer personalized promotions and navigate customers through stores, enhancing engagement and satisfaction.
IoT in Healthcare
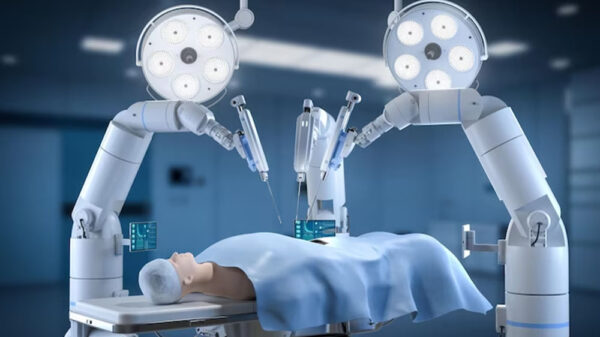
In healthcare, IoT is revolutionizing patient care and medical management. Wearable devices track vital signs, allowing healthcare providers to monitor patients remotely and deliver timely interventions. IoT-enabled hospital equipment ensures efficient asset management and improved patient outcomes, making healthcare more accessible and effective.
IoT in Smart Cities
IoT is a cornerstone of smart city initiatives, improving urban living through intelligent infrastructure. Connected sensors monitor traffic patterns, optimize energy usage, and enhance waste management systems. These advancements reduce resource consumption, lower operational costs, and improve the quality of life for residents.
IoT and Predictive Analytics
IoT generates vast amounts of data, which, when combined with predictive analytics, allows businesses to anticipate trends and prevent potential issues. For example, IoT sensors in industrial settings can predict equipment failures, enabling preemptive maintenance. This foresight minimizes disruptions and enhances productivity.
The Role of Edge Computing in IoT
Edge computing complements IoT by processing data closer to its source, reducing latency and bandwidth usage. This is particularly crucial for applications that require real-time decision-making, such as autonomous vehicles or smart manufacturing. The integration of edge computing ensures faster and more reliable IoT operations.
IoT in Retail and E-Commerce
Retailers and e-commerce platforms use IoT to enhance inventory management, optimize supply chains, and improve customer experiences. IoT-enabled devices provide real-time inventory updates, reducing stockouts and overstock situations. Automated warehouses equipped with IoT streamline order fulfillment processes, ensuring timely deliveries.
Challenges in IoT Adoption
Despite its benefits, IoT faces challenges such as security vulnerabilities, data privacy concerns, and high implementation costs. With the increasing number of connected devices, ensuring robust cybersecurity measures and complying with data protection regulations is essential for businesses to safeguard user trust.
IoT and Sustainability
IoT contributes to sustainability efforts by optimizing resource usage and reducing waste. Smart energy grids monitor consumption patterns and distribute energy efficiently, while IoT-enabled agricultural devices optimize water usage and crop management. These applications align with global sustainability goals and reduce environmental impact.
IoT in Autonomous Systems
Autonomous systems, such as self-driving cars and drones, heavily rely on IoT for seamless operation. Sensors and communication networks enable these systems to navigate and make decisions in real-time. The integration of IoT in autonomous technologies enhances safety, efficiency, and reliability.
IoT Standards and Interoperability
The lack of standardized protocols and interoperability among IoT devices remains a challenge for businesses. Efforts to establish universal standards are underway, aiming to ensure seamless communication and integration across devices from different manufacturers. This development will drive broader IoT adoption.
The Future of IoT in Business
The future of IoT lies in its integration with advanced technologies such as AI, blockchain, and 5G. These innovations will enhance IoT capabilities, enabling more sophisticated data analysis, secure transactions, and faster communication. As IoT evolves, its applications will expand, creating new opportunities for businesses to innovate.
Conclusion: A Connected World
The Internet of Things is transforming how businesses operate, making processes more efficient and customer experiences more personalized. By bridging the gap between the physical and digital worlds, IoT is driving innovation across industries. As businesses continue to adopt IoT technologies, they will unlock new potential for growth, sustainability, and enhanced customer satisfaction, solidifying IoT’s role as a cornerstone of modern business strategies.