The Importance of Biodiversity
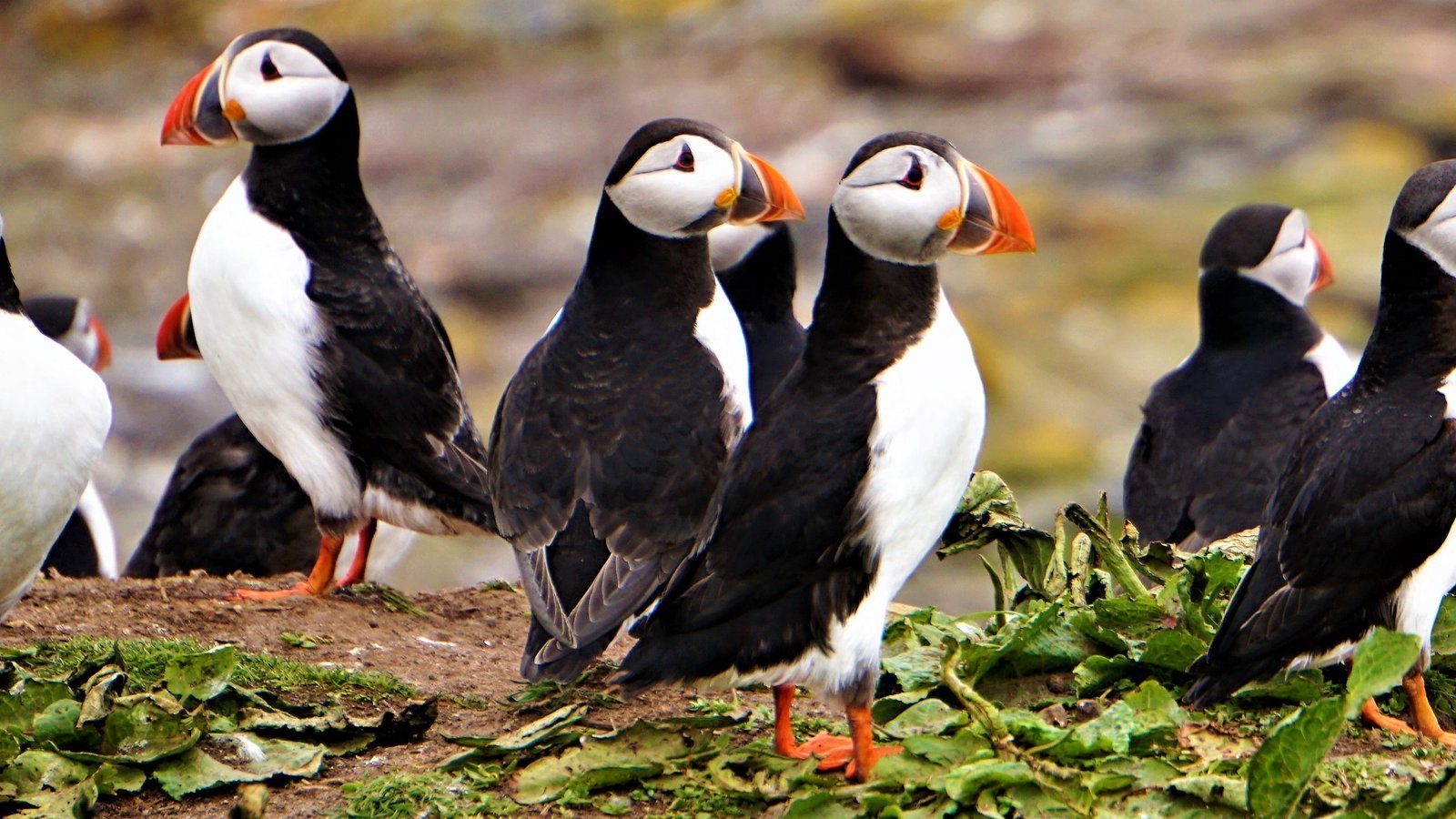
Biodiversity is the foundation of life on Earth. It encompasses the variety of species, ecosystems, and genetic diversity that exist on our planet. It is essential for the health and stability of our ecosystems, providing us with clean air, water, and food. Biodiversity also plays a crucial role in supporting our economies, providing us with resources for medicine, agriculture, and tourism.
The Current State of Biodiversity
Unfortunately, our planet is currently facing a biodiversity crisis. Species extinction rates are now estimated to be 1,000 times higher than the natural background rate. This is largely due to human activities such as habitat destruction, pollution, climate change, and overexploitation of natural resources.
The Extinction Crisis
The extinction crisis is not just a concern for conservationists, but for all of humanity. When a species goes extinct, it is lost forever, along with its unique genetic information and potential benefits to humans. It also disrupts the delicate balance of ecosystems, leading to the loss of other species and potentially impacting our own survival.
The Latest Findings
Recent studies have shed light on the severity of the extinction crisis. One study published in the journal Science found that up to one million species are at risk of extinction, many within decades. This includes iconic species such as elephants, tigers, and polar bears, as well as lesser-known species that play important roles in their ecosystems.
Causes of Species Extinction
There are several key factors driving species extinction:
- Habitat Loss: The destruction and fragmentation of natural habitats due to deforestation, urbanization, and agriculture.
- Pollution: The release of harmful chemicals into the environment, including pesticides, industrial waste, and plastic pollution.
- Climate Change: The alteration of temperature and precipitation patterns, leading to shifts in ecosystems and the loss of suitable habitats.
- Overexploitation: The unsustainable harvesting of species for food, medicine, and trade.
The Consequences of Species Extinction
The loss of biodiversity has far-reaching consequences:
- Ecological Impact: The loss of species disrupts the intricate web of life, leading to imbalances in ecosystems and the potential collapse of entire food chains.
- Economic Impact: The loss of biodiversity can have significant economic consequences, affecting industries such as agriculture, forestry, and tourism.
- Health Impact: Biodiversity loss can increase the spread of diseases, as well as reduce the availability of natural resources for medicine and healthcare.
- Cultural Impact: Many cultures around the world have deep connections to nature and rely on biodiversity for their traditional practices and livelihoods.
The Need for Action
Addressing the extinction crisis requires collective action at all levels:
- Conservation Efforts: Protecting and restoring habitats, implementing sustainable practices, and establishing protected areas.
- Policy Changes: Enacting laws and regulations that promote biodiversity conservation and sustainable development.
- Education and Awareness: Raising awareness about the importance of biodiversity and the actions individuals can take to protect it.
Conclusion
The extinction crisis is a pressing issue that requires immediate attention. We must recognize the value of biodiversity and take action to protect and restore it. By doing so, we can ensure a sustainable future for ourselves and future generations.