The Impact of Scorching Temperatures on Society
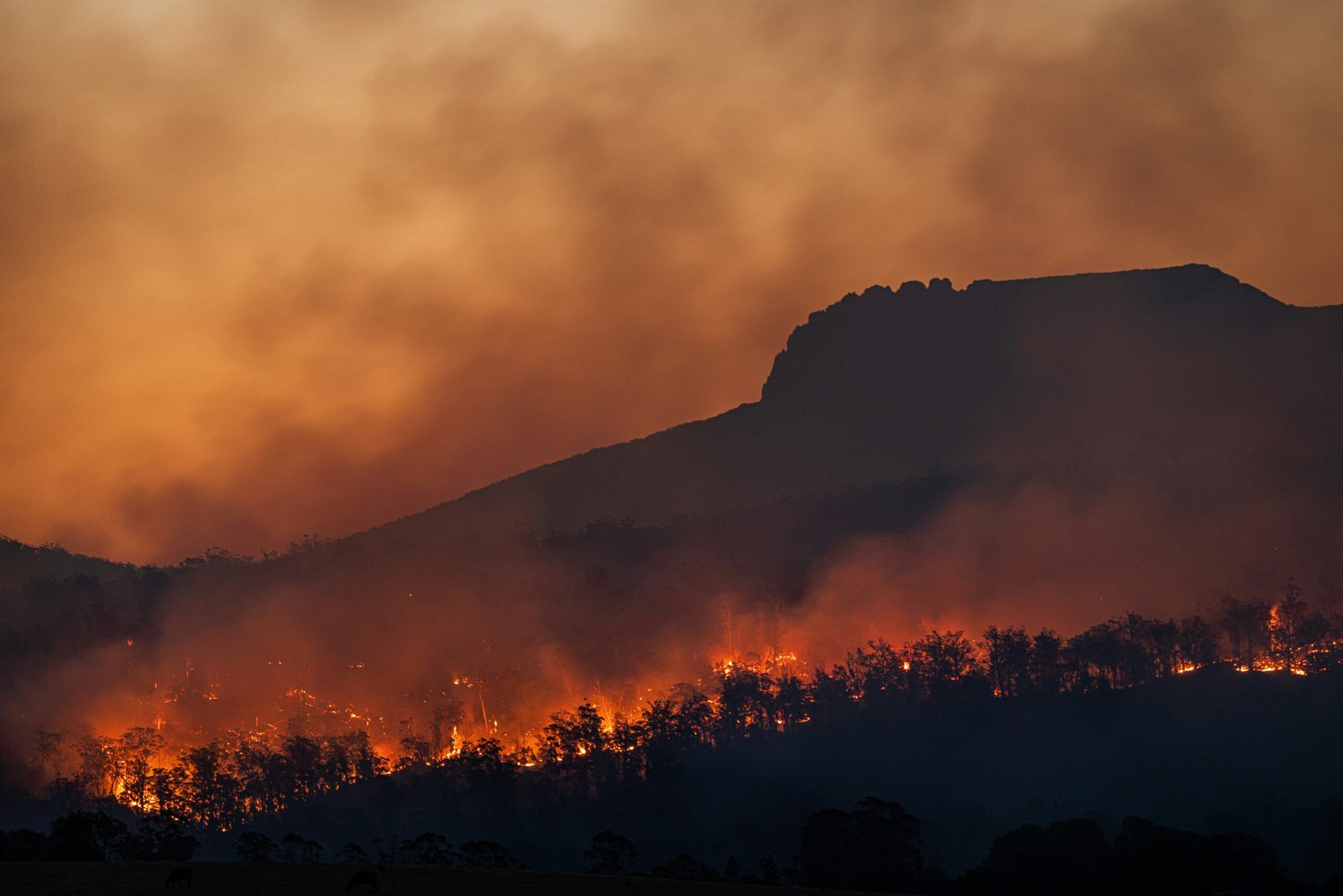
In recent years, the surge in extreme heat events across the globe has had devastating effects on human health, infrastructure, and ecosystems. The severity of these heatwaves is underscored by alarming statistics, with hundreds of deaths reported during particularly intense periods. For instance, Europe’s 2019 heatwave resulted in over 1,500 deaths in France alone, while the Pacific Northwest in the United States experienced record-breaking temperatures in 2021, leading to significant mortality rates.
These extreme temperatures place immense strain on public health systems. Hospitals and emergency services are often overwhelmed by the influx of heat-related illnesses, ranging from heat exhaustion and heatstroke to exacerbations of chronic conditions such as cardiovascular and respiratory diseases. Vulnerable populations, including the elderly, the homeless, and individuals with preexisting health conditions, are particularly at risk. The compounded stress on healthcare facilities highlights the critical need for robust, heat-adaptive public health strategies.
Beyond health, the societal implications of scorching temperatures are extensive. Economically, heatwaves disrupt daily activities and productivity, leading to substantial economic losses. Agricultural sectors suffer from reduced crop yields and livestock productivity, threatening food security. Furthermore, increased energy demands for cooling exacerbate power grid stress, leading to frequent blackouts and further economic disruption.
Radley Horton, a climate scientist at Columbia University, emphasizes that the frequency and intensity of these extreme heat events are not anomalies but rather a consequence of ongoing climate change. Horton explains that rising global temperatures, driven by increased greenhouse gas emissions, are making heatwaves more severe and frequent. This scientific perspective underscores the urgent need for adaptive measures, including improved infrastructure, public health preparedness, and comprehensive climate policies to mitigate the impacts of extreme temperatures.
As society grapples with these challenges, it becomes evident that current measures are insufficient to keep pace with the escalating threat posed by extreme heat. The insights provided by experts like Horton highlight the necessity for immediate and sustained action to adapt to a rapidly changing climate.
Challenges and Solutions in Adapting to Extreme Heat
As global temperatures continue to rise, societies worldwide are grappling with significant challenges in adapting to extreme heat. One of the primary issues is the inadequacy of existing infrastructure and urban planning. Many cities lack sufficient cooling centers, forcing vulnerable populations to endure dangerous heat levels without relief. Additionally, the scarcity of green spaces exacerbates the urban heat island effect, leading to even higher temperatures in densely populated areas. Outdated building designs that fail to incorporate modern cooling technologies further compound this problem, making it difficult to maintain comfortable indoor temperatures during heatwaves.
Effective policy and governance are crucial in addressing these heat-related challenges. Comprehensive climate action plans at local, national, and global levels are essential to mitigate the impacts of extreme heat. These plans should prioritize the development and maintenance of cooling centers, the expansion of green spaces, and the implementation of updated building codes that mandate the use of heat-resistant materials. By fostering collaboration between government entities, non-profits, and the private sector, these initiatives can enhance community resilience against rising temperatures.
Several strategies can be employed to bolster community resilience to extreme heat. Implementing heat early warning systems can provide timely alerts to the public, allowing individuals to take necessary precautions. Public awareness campaigns are also vital, as they educate communities about the dangers of extreme heat and the steps they can take to protect themselves. Promoting the use of heat-resistant building materials, such as reflective roofing and advanced insulation, can significantly reduce indoor temperatures and energy consumption.
Innovative technological solutions offer promising avenues for coping with extreme heat. Advanced cooling systems, including energy-efficient air conditioning and passive cooling techniques, can help maintain comfortable temperatures without exacerbating energy demand. Climate-smart agriculture practices, such as drought-resistant crops and optimized irrigation methods, can ensure food security in the face of increasing temperatures. Insights from Radley Horton underscore the scientific basis for these adaptive strategies, highlighting the urgent need for immediate and sustained action to safeguard communities and ecosystems from the escalating heat crisis.